Air Pollution
Air Pollution
go back to Contents of entire course...
Smog
Control of Air Pollution
Air Inversion
Global Warming
Greenhouse Gases
External Links
adapted to HTML from lecture notes of Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tulane University
Smog
Smoke plus Fog (based on Britain's experience) (Grey smog)
- Photochemical Smog - brown air. (This is what we have in the U.S.) Results from exhausts from cars, buses and trucks.
- Nitrogen Oxide + Oxgen + Hydrocarbons + Sunlight -- > Ozone
- 6ppm ozone is deadly - We need ozone in stratosphere; at lower altitudes, however, it can kill.
- Sulfurous Fog- gray air.
- Dominantly from burning coal with a significant pyrite content. The fogs of London in the past were actually sulfuous fog. This type of smog is no longer common in London as a result of environmental regulations on burning coal.
Control of Air Pollution Automobiles
Coal Main problem is the sulfur dioxide it produces upon burning.
Solutions:
Air Inversion
In valleys or on the lee side of mountains, air inversion may occur. A warmer air mass moves above cooler air, trapping the cooler, denser air underneath and increasing the severity of air pollution. Los Angeles is a good example of this, where warm desert air from the east comes over the mountains to the east of Los Angeles and lies over the cooler Pacific Ocean air. The cooler air is trapped because it cannot rise through the less dense warm air above it, and the pollution in the cold air accumulates.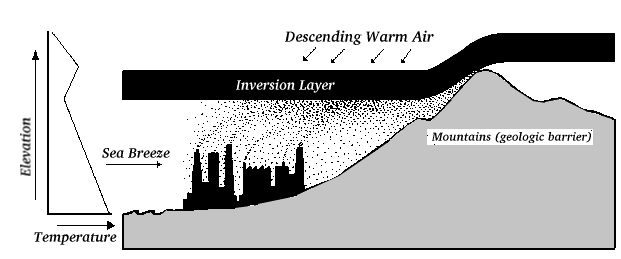
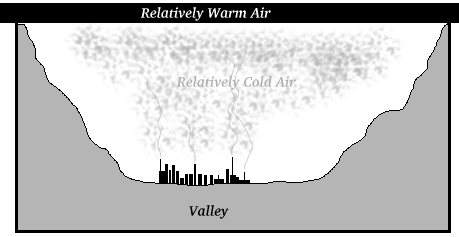
A similar situation arises in mountain valleys where warm air overlies the colder air which accumulates in the valleys.
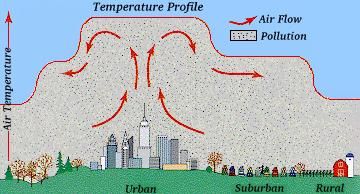
Also, cities tend to form featuers known as heat islands or dust domes, which tend to collect warm air filled with pollutants, and help spread it out over nearby suburbs.
Global Warming
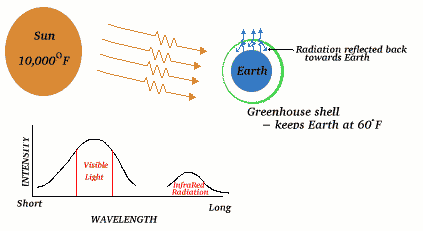
- The increase in CO2 is anthropogenic (related to human activities). It is mostly due to the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Roughly 60% of total
- Burning Fossil Fuels
- Deforestation
- Methane (CH4): 15% of total
- Coal Mines
- Termites
- Wetlands
- Rice Paddies
- Cattle
- Subpolar Soil and Wetlands (Methane Hydrate)
- Air Pollution
- A collection of Links on Air Pollution: http://www.deb.uminho.pt/fontes/enviroinfo/air.htm
- NASA Climate News page: http://www.climatenews.com/
- The Union of Concerned Scientists have a global warming page: http://www.ucsusa.org/warming/index.html
- The Sierra Club page: http://www.toowarm.org/home.html
- The Environmental Protection Agency site on Global Warming: http://www.epa.gov/globalwarming/
- This is a page arguing against global warming: http://www.webaxs.net/~noel/gwarming.htm
- This page details the myths and misarguments by both sides of the global warming debate: http://members.aol.com/jimn469897/warming.htm
| Gases contributing to Anthropogenic Greenhouse Effect | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gas | Rate of Increase (% per year) |
Relative Contribution(%) |
| CO2 | 0.5 | 60 |
| CH4 | 1 | 15 |
| N2O | 0.2 | 5 |
| O3 | 0.5 | 8 |
| CFC-11 | 4 | 4 |
| CFC-12 | 4 | 8 |
Global Warming has been studied extensively, and currently, a large percentage of the scientific community have reached a consensus on various issues related to global warming.
They are listed below:
| Scientific Consensus on Global Warming | |
|---|---|
| Statement | Consensus |
| Fundamental Physics | 90+% |
| Added greenhouse gases add heat | 90+% |
| Added gases are anthropogenic | 90+% |
| Reduction of uncertainty will require a decade | 90+% |
| Full recovery will require many centuries | 90+% |
| Large stratospheric cooling | 90+% |
| Precipitation will increase | 90% |
| Reduction of sea ice | 90% |
| Warming in arctic | 90% |
| Rise in sea level | 90% |
| Local details of global change | ? |
| Tropical storms increase | ? |
| Details of next 25 years | ? |
Greenhouse Gases
External Links
Global Warming
A Collection of sites that NASA put together about global warming: http://gcmd.gsfc.nasa.gov/faq/globwarm.html

